What is a DAX?
The DAX is a stock exchange index consisting of the 30 major German blue chip companies trading on the Frankfurt stock market . it's a complete return index. Prices are taken from the Xetra trading venue.
The DAX, short for Deutscher Aktienindex, is a major stock market index in Germany. It represents the performance of the 40 largest and most liquid companies listed on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange. Here’s a detailed overview:
Index Overview
- Name: DAX (Deutscher Aktienindex)
- Type: Stock Market Index
- Country: Germany
- Exchange: Frankfurt Stock Exchange (Frankfurter Wertpapierbörse)
- Established: 1988
Constituents
The DAX index includes 40 of the largest and most traded companies on the Frankfurt Stock Exchange. These companies span various industries, including automotive, chemicals, technology, finance, and consumer goods. Some of the prominent companies typically included are:
- Volkswagen AG
- SAP SE
- Siemens AG
- Allianz SE
- BMW AG
The composition of the DAX is periodically reviewed and updated to reflect changes in the market capitalization and liquidity of the constituent companies.
Calculation Method
- Market Capitalization-Weighted: The DAX is a market capitalization-weighted index, meaning that companies with higher market capitalizations have a greater influence on the index’s performance.
- Free-Float Adjusted: The index uses free-float capitalization, which adjusts the market capitalization based on the number of shares available for trading, excluding shares held by insiders and other strategic holders.
Purpose and Use
- Benchmark: The DAX serves as a key benchmark for the German stock market, providing an indicator of the overall performance of the largest companies in Germany.
- Investment: It is used by investors and fund managers to gauge market trends and performance. Many investment funds, ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds), and financial products are designed to track the DAX.
Historical Performance
- 1988: The DAX was established on July 1, 1988, with a base value of 1,000 points.
- Performance: Over the years, the DAX has experienced various market cycles, reflecting both economic growth and downturns. It has grown significantly since its inception, becoming one of the leading stock market indices in Europe.
Significance
- Economic Indicator: The DAX is often used as a barometer for the health of the German economy, given that it includes major companies that are representative of various sectors.
- Global Influence: As one of the major European indices, the DAX is closely watched by international investors and analysts. It often reflects global economic trends and market sentiment.
Recent Developments
- Expansion to 40 Companies: In September 2021, the DAX expanded from 30 to 40 companies, increasing its representation of the German market.
- Digital Transformation: The index includes companies that are at the forefront of technological and digital transformation, reflecting the evolving nature of the German economy.
Investment Products
- ETFs and Mutual Funds: Several financial products are based on the DAX, including ETFs and mutual funds, allowing investors to gain exposure to the index’s performance.
- Derivatives: Futures and options contracts based on the DAX are available for trading, providing tools for hedging and speculation.
How to analyze dax data in python?
!pip install yfinance
How to import dax data from yahoo finance?
import yfinance as yf
progress=False)
How to get a dax returns in python?
DAX['Returns'] = np.log(DAX['Close'] / DAX['Close'].shift(1))
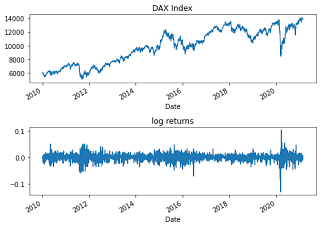
How to plot log return and dax data in python?
plt.tight_layout()
| Open | High | Low | Close | Adj Close | Volume | Returns | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Date | |||||||
| 2010-01-04 | 5975.520020 | 6048.299805 | 5974.430176 | 6048.299805 | 6048.299805 | 104344400 | NaN |
| 2010-01-05 | 6043.939941 | 6058.020020 | 6015.669922 | 6031.859863 | 6031.859863 | 117572100 | -0.002722 |
| 2010-01-06 | 6032.390137 | 6047.569824 | 5997.089844 | 6034.330078 | 6034.330078 | 108742400 | 0.000409 |
| 2010-01-07 | 6016.799805 | 6037.569824 | 5961.250000 | 6019.359863 | 6019.359863 | 133704300 | -0.002484 |
| 2010-01-08 | 6028.620117 | 6053.040039 | 5972.240234 | 6037.609863 | 6037.609863 | 126099000 | 0.003027 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 2021-02-19 | 13941.400391 | 14026.179688 | 13892.719727 | 13993.230469 | 13993.230469 | 72974000 | 0.007626 |
| 2021-02-22 | 13858.559570 | 13975.080078 | 13802.549805 | 13950.040039 | 13950.040039 | 66035300 | -0.003091 |
| 2021-02-23 | 13984.980469 | 13989.240234 | 13664.709961 | 13864.809570 | 13864.809570 | 88194700 | -0.006128 |
| 2021-02-24 | 13855.849609 | 13998.299805 | 13855.849609 | 13976.000000 | 13976.000000 | 68922400 | 0.007988 |
| 2021-02-25 | 14045.019531 | 14051.009766 | 13879.169922 | 13879.330078 | 13879.330078 | 95431900 | -0.006941 |
2824 rows × 7 columns



0 Comments